Describe the Mechanics of Inhalation and Exhalation
When a person inhales the diaphragm and the muscles between the ribs contract and expand the chest cavity. Both Inhalation and Exhalation occur due to.
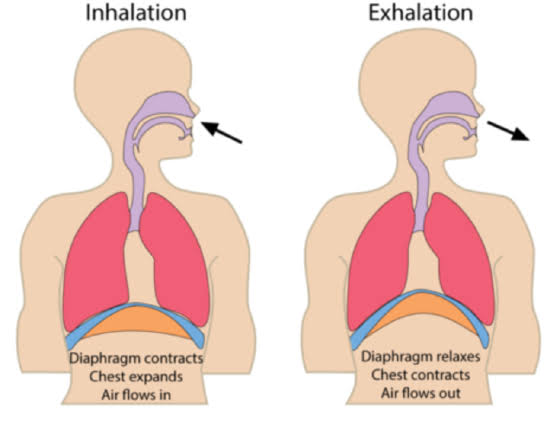
Difference Between Inhalation And Exhalation Diferr
Inspiration - air flows into lungs.
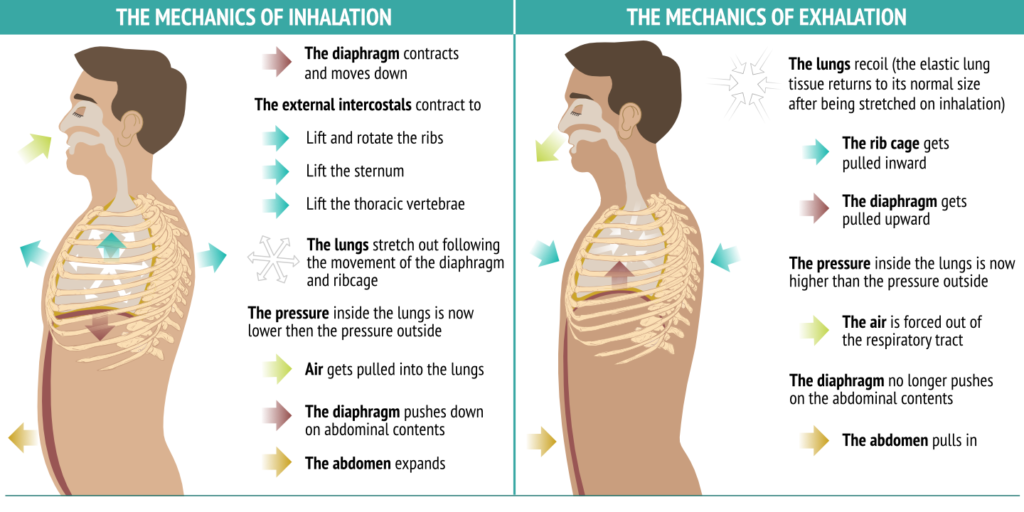
. The intercostal muscles relax so the ribs move inwards and downwards under their own weight. The process of inhalation occurs due to an increase in the lung volume diaphragm contraction and chest wall expansion which results in a decrease in lung pressure in comparison to the. Exhalation is referred to as exhaling on flushing out carbon dioxide out of the body.
Expiration occurs when the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles relax. Inhalation is the process of intake of air into lungs whereas exhalation is the process of letting air out from lungs. The law states that if the volume increases then the pressure must decrease or vice versa.
This relationship is often written algebraically as PV constant or P 1 V 1 P 2 V 2. This is brought about due to the contraction of respiratory muscles. The action of breathing in and out is due to changes in pressure within the chest thorax.
Both equations state that the product of the pressure and volume remains the same. Inspiration occurs via active contraction of muscles such as the diaphragm whereas expiration tends to be passive unless it is forced. -process of exhalation occurs due to an elastic recoil of the lung tissue which cause a decrease in volume resulting in increased pressure in comparison to the.
During inspiration the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles contract causing the rib cage to expand and move outward and expanding the thoracic cavity and lung volume. When the chest cavity expands the pressure in the chest is lowered to a level below that of the air pressure outside. It is the process of air flowing into the lungs during inspiration inhalation and out of the lungs during expiration exhalation.
These mechanisms depend on pressure gradients as well as the muscles in the thoracic cavity. Inspiration occurs when the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles contract. Vt IRV ERV Reserve Volume VC TLV.
Boyles Law describes the relationship between the pressure P and the volume V of a gas. Breathing is the physical process of inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide. Expiration breathing out The diaphragm relaxes and moves back to its domed shape.
Breathing consists of two phases called inhalation and exhalation. Tidal volume multiplied by the respiratory rate is minute ventilation which is one of the most important indicators of. The mechanics of breathing Air moves in and out of the lungs in response to differences in pressure.
The breathing mechanisms of most mammals include two parts. However several other supporting muscles and organs aid in carrying out the inhalation and exhalation process. The following table contains the striking differences between the inhalation and exhalation processes.
Here we explain the mechanics of breathing and how breathing is regulated at rest. In order for air to be drawn into the lungs during inhalation the volume of the thorax must increase. Describe and diagram the mechanics of inhalation and exhalation including liquids and chambers and muscles involved.
1Describe and diagram the mechanics of inhalation and exhalation including gasses liquids and chambers and muscles involved. Mechanism of Inhalation and Exhalation. Pulmonary ventilation is commonly referred to as breathing.
The mechanics of breathing follow Boyles Law which states that pressure and volume have an inverse relationship. DESCRIBE the different respiratory volumes and EXLAIN HOW they are produced. Mechanics Mechanism Of Breathing.
Inhalation is the term used to define the taking-in process of oxygen. This action is also known as external respiration and is created by the muscles of the chest and the diaphragm changing the size of the chest cavity and air pressure. It is a mechanical process that depends.
The lung is the primary organ that actively takes part in respiration. O Define the Lung Volumes. When this happens air flows in through the airways from a high pressure to low pressure and inflates the lungs.
Pressure Relationships in the Thorax. -occurs due to an increase in the lung volume diaphragm contraction and chest wall expansion which results in a decrease in lung pressure in comparison to the atmosphere. However the details of breathing between birds and mammals differ substantially.
Expiration - gases exit lungs. The diaphragm contract during the inhalation and get flattens by moving down while they relax during exhalation and turned into dome-shaped by moving up. When the air pressure within the alveoli exceeds atmospheric pressure air is blown from the lungs expiration.
The mechanism of breathing involves two main processes. Inhalation is an active process though exhalation is a passive process. 2 Phases of Breathing.
The terms inspiration and expiration are also used often to refer to the breathing process. The ability of the alveoli to expand when air is drawn in during inhalation. When the air pressure within the alveolar spaces falls below atmospheric pressure air enters the lungs inspiration provided the larynx is open.
-when the diaphragm contracts. Oxygenated air taken in during inhalation diffuses across the surface of the lungs into the bloodstream while carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the lungs and is expelled during exhalation. The sarcomere is going to contract and go towards the center so it flattens it out and it pulls it down which pulls the lungs down.
Breathing or pulmonary ventilation has two phases - inspiration or inhalation and expiration or exhalation. Air rushes in airway. 2 phases act to ventilate the lungs.
Explain the mechanism of breathing. Respiration refers to the exchange of gases between a living organism and its environment while breathing is the process that moves air into and out of the lungs Thibodeau and Patton 2005. The mechanism of breathing obeys Boyles law which states that that in a closed space pressure and volume is inversely related as the volume.
The processes of inspiration breathing in and expiration breathing out are vital for providing oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide from the body. Following is a detailed explanation for the same. During normal breathing the volume of air cycled through inhalation and exhalation is called tidal volume VT and is the amount of air exchanged in a single breath.
Pulmonary ventilation consists of the process of inspiration or inhalation where air enters the lungs and expiration or exhalation where air leaves the lungs. Atmospheric pressure Patm - pressure gas exerts on surface of earth 760 mm Hg 1 atm. Air flows because of pressure differences between the atmosphere and the gases inside the lungs.
The diaphragm contracts and flattens and the intercostal muscles contract to pull the ribs up and out.

Difference Between Inhalation And Exhalation In Tabular Form

How To Combine Breath And Movement In Your Yoga Practice Sequence Wiz
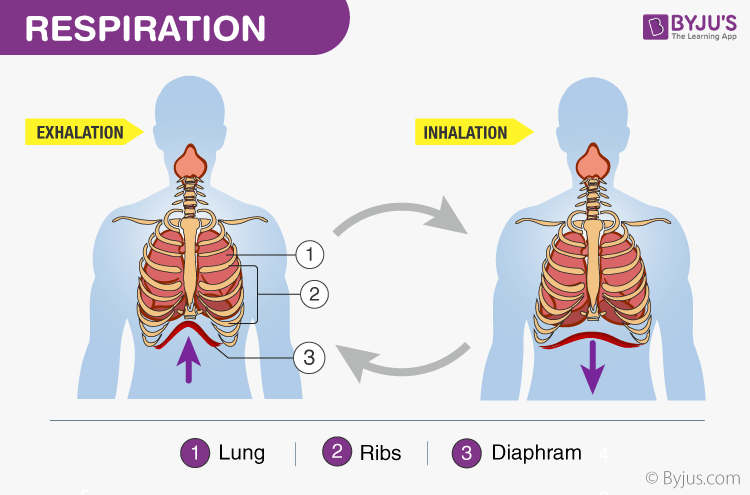
Mechanism Of Breathing Explore Mechanism Of Respiration In Detail
No comments for "Describe the Mechanics of Inhalation and Exhalation"
Post a Comment